If you’re like many searching for that certain ultra effective fat burning workout, you may end up on the wrong side of confusion. Perhaps you read a book which promises results. Maybe a recent magazine article told you something else, or the trainer at the local gym recommended a completely different approach.
The truth is, the days of long, boring cardio need to be put to rest. People are extremely busy today, and using outdated methods that require a large amount of time is a sure way to kill initiative. But a number of studies have indicated that metabolic resistance training is a highly effective training technique for fat loss. Also known as MRT, it consists of fast-paced weight-training circuits arranged so that muscles are worked in an alternating (non-competing) sequence – an upper-body exercise will be followed by a lower-body exercise. Anytime you use circuits or supersets to train with an elevated heart rate with insufficient recovery, you are doing metabolic resistance training.
MRT Results
The efficiency of MRT training is now adequately researched and documented. Studies prove that combining a sensible eating plan with MRT yields nearly 20 percent more fat loss than diet and aerobic exercise and nearly 30 percent more than those who only diet. That is a pretty amazing difference.
MRT sessions are so efficient because you move quickly from exercise to exercise, burning more fat in less time. And a giant upside to it is the “afterburn effect,” a result of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption, or EPOC. MRT keeps the body’s metabolic rate elevated for up an astounding 38 hours, according to a study published in the March 2002 issue of “European Journal of Applied Physiology,”
Increased testosterone is another benefit. The primary exercises used in MRT work multiple large muscle groups at once. This stimulates the release of testosterone, which is a naturally produced steroid hormone that is essential for the muscle-building process.
Combining heavy compound movements with minimal rest also effectively stimulates the release of natural growth hormone, which builds muscle, burns fat and helps you recover faster for the next workout.
How to perform MRT
The best strategy with MRT is to alternate between large upper- and lower-body movements and use relatively shorter rest periods so that one muscle group can rest while you work the opposing muscles. This is critical to increasing the caloric burn and total work performed. A good strategy to doing this is using super-sets or tri-sets of circuits which will make you work harder and also get better results.
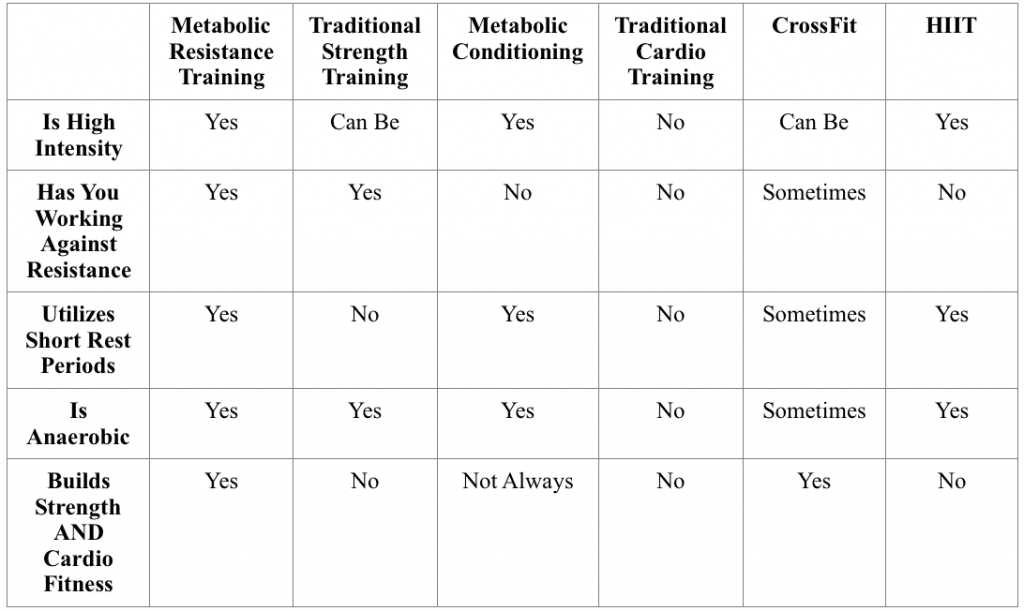
How does this differ from other intense workout styles?
Here’s a quick comparison.
Here are three examples:
MRT Workout 1
Barbell push press or body weight pushups x 10reps
RDL’s x 10 reps each exercise
DB squats x 20 reps
Rest 20 to 40 seconds and repeat for a total of three rounds.
MRT Workout 2
Assisted pullups x 10 reps
2 pushups/2 burpees x 45 seconds
Kettle bell swings x 45 seconds
Jump squats x 30 seconds
Rest 20 to 40 seconds and repeat for a total of three rounds.
MRT Workout 3
Bar deadlifts x 8 reps
Bar shoulder push press x 8 reps
Bench step ups x 1 minute
Bar front pullups x 8 reps
Rest 20 to 40 seconds and repeat for a total of three rounds.
The demand placed on the body forces it to burn fat. It’s all about obtaining a metabolic response and burning tons of calories in a brief amount of time.
Conclusion
MRT training takes out a lot of the stress off the joints, unlike running or sprinting. For example, by running one mile, you could end up doing around 1,500 steps at 2-4 times your body weight per stride. With a ten mile run, this multiplies to 15,000 reps of knee wrecking force.
As well, there are fundamental differences between long distance running and even sprinting. Sprinters have more highly muscled bodies because they train their anaerobic system through high intensity interval training. Long distance runners, on the other hand, run at a steady aerobic pace for hours at a time.
Training for fat loss needs to include:
1) An emphasis on building muscle.
2) Making muscle work hard in multiple movements and multiple planes of motion
3) Make muscles work fast and in a powerful fashion.
4) Make the metabolism work through short rest periods, high work density by ramping up energy expenditure during and post-workout.
5) Add in non traditional interval training of the entire body hard, working more muscle and more movements than traditional cardio.
So doing less traditional cardio and inserting MRT training into your routine will help you get results fast.